Testing focuses on a few details: Dimensional accuracy, winding precision, and printing quality. Winding precision is a visual test where I check to make sure the filament works well on the spool, without any crossovers that can cause snags while printing.
Print quality is done using a CNET calibration test that I use to test all of the 3D printers I review. When checking for filament quality, I’m looking for noticeable roughness and missing filament where moisture or other contaminants have interrupted the process of melting and cooling.
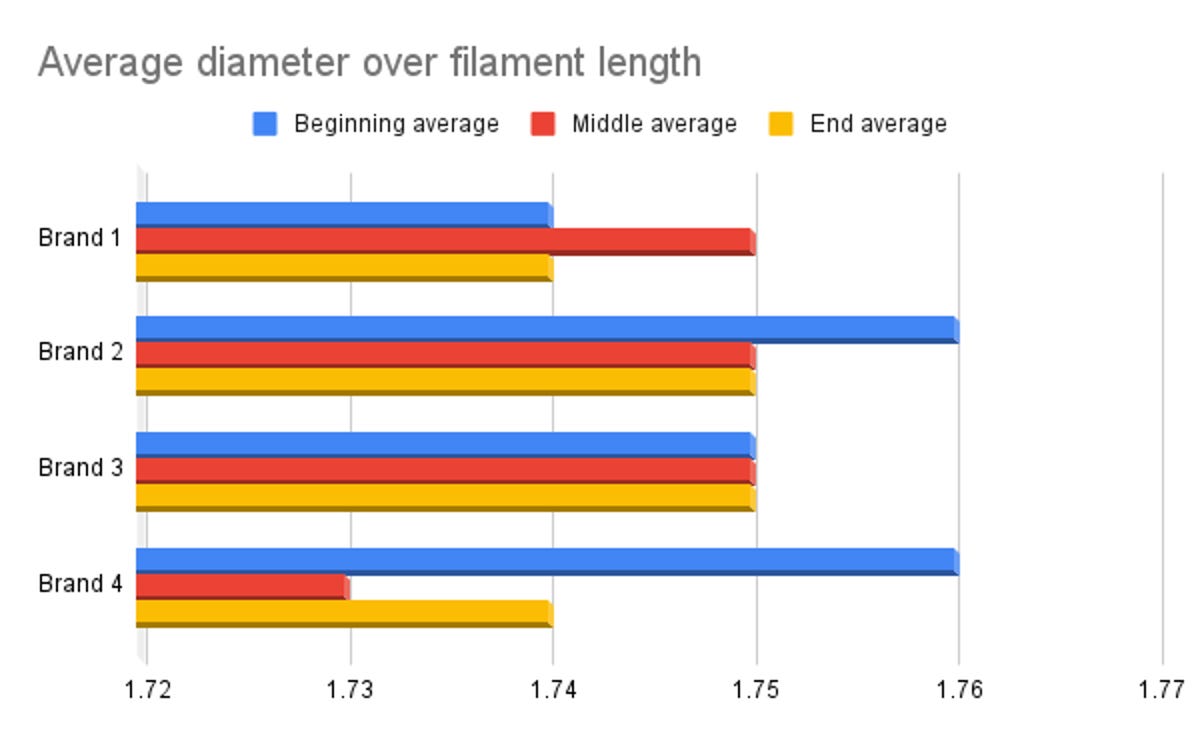
Dimensional accuracy is perhaps the most important test as it measures the consistency of filament. As you move along, the filament changes in diameter and will cause the 3D printer to over- or under-extrude filament. This creates noticeable scarring in your model, or worse, complete failure. You want the material to have the same diameter the whole way through.
To measure the accuracy, I take a 5-meter (16.4-foot) piece of filament from the beginning, middle and end of the roll and measure the diameter at four equally spaced points. I then add up all of those measurements and divide the total by 12 — the total number of measurements taken — to give me an average across the roll. Most modern printers use 1.75mm filament, so you want the filament to be as close to that as possible.
Great filament has a variance of plus or minus 0.02mm, good filament is plus or minus 0.03mm and rough filament is anything plus or minus 0.05mm. All of the filaments we have recommended here are at least 0.03mm on average.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours